Golden Raisins: Why They Stand Out Among Dried Fruits
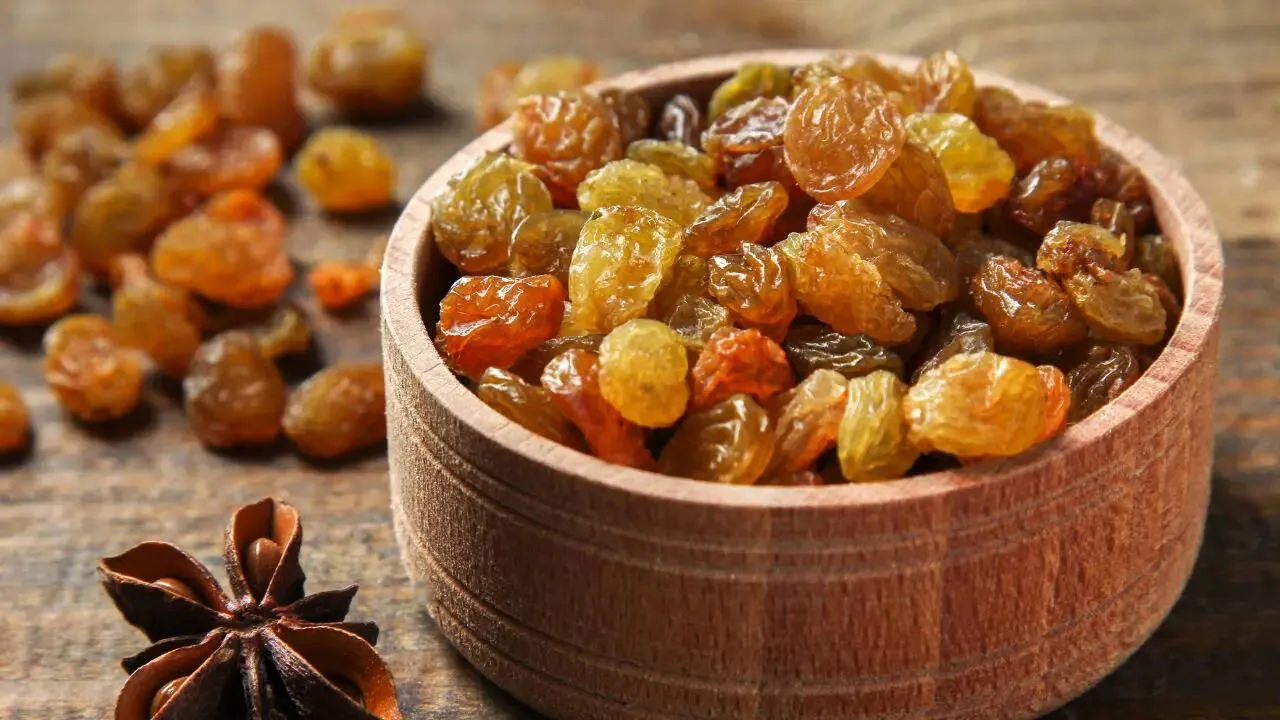
Golden raisins are one of the most delightful and nutritious forms of dried fruit enjoyed across the world. With their soft golden appearance, naturally sweet flavor, and chewy texture, they have become a favorite ingredient in both traditional recipes and modern healthy diets.
Unlike many processed snacks, raisins offer a naturally occurring sweetness along with essential nutrients. Their growing popularity is largely due to their convenience, long shelf life, and ability to enhance both sweet and savory dishes.
The purpose of this article is to provide a detailed exploration of golden raisins—covering what they are, their fascinating history, how they are made, where they are produced, how they compare to other raisin varieties, and their impressive nutritional profile.
What Are Golden Raisins?
Raisins are essentially dried grapes that maintain a bright golden-yellow color rather than turning dark brown or black. They are commonly known by another popular name: sultanas.
Raisins differ from regular raisins mainly in their drying process and appearance. While dark raisins are usually sun-dried, raisins are dried under controlled conditions, which helps them retain their lighter shade.
Some key characteristics of golden raisins include:
- Mild and pleasant sweetness
- Plump and juicy texture
- Light golden color
- Softer chew compared to darker raisins
Because of these qualities, raisins are widely appreciated as both a snack and a versatile culinary ingredient.
History and Origin of Golden Raisins
The story of raisins begins thousands of years ago. Historical evidence suggests that grapes were being dried for food as early as 2000 BC, making raisins one of the oldest preserved fruits in human history.
Ancient Mediterranean civilizations, including early Greeks and Egyptians, discovered that drying grapes in the sun created a sweet, long-lasting food source. Raisins became valuable because they were:
- Easy to store
- Portable for travelers and traders
- Naturally sweet without added sugar
However, golden raisins as we know them today developed much later. Centuries after traditional raisins were popularized, producers began experimenting with methods to preserve the lighter color of grapes during drying.
This led to the introduction of sulfur treatment, which helped prevent browning and allowed raisins to maintain their signature bright appearance.
How Golden Raisins Are Made
Raisins go through a unique production process that distinguishes them from regular sun-dried raisins. Their color, texture, and flavor are shaped by three key steps:
Grape Selection
Raisins are usually made from green, seedless grapes, often the Thompson variety. The quality of grapes plays a major role in determining the final product’s taste and texture.
High-quality grapes produce raisins that are:
- Sweeter
- Softer
- More flavorful
- Uniform in size
The selection process ensures that only the best grapes are used for drying.
Drying Process
Unlike regular raisins that are dried directly under the sun, golden raisins are produced through controlled dehydration.
This method involves drying grapes in a regulated environment where temperature and humidity are carefully monitored. Controlled drying helps maintain:
- A plumper texture
- A lighter appearance
- A sweeter, more delicate flavor
Drying also concentrates the natural sugars and nutrients found in grapes, making raisins energy-rich and nutrient-dense.
Color Preservation of Golden Raisins
One of the most important steps in golden raisin production is preserving their golden color. This is done using a small amount of sulfur dioxide treatment.
Sulfur dioxide helps:
- Prevent grapes from turning dark during drying
- Maintain a bright golden hue
- Extend shelf life
This is the primary reason raisins remain lighter than regular raisins, which naturally darken when dried in sunlight.
Where Golden Raisins Are Produced
. Raisins are produced in many grape-growing regions around the world. Countries with warm climates and strong agricultural industries are major suppliers.
Some of the leading production areas include:
United States (California)
California is one of the world’s largest raisin-producing regions, known for high-quality golden raisins.
Turkey
Turkey is a major exporter of raisins and produces premium sultanas for international markets.
Greece
Greek golden raisins are valued for their Mediterranean flavor and traditional cultivation methods.
Australia
Australia also contributes significantly to the global raisin industry, producing sweet and consistent varieties.
The taste and quality of golden raisins can vary depending on:
- Climate conditions
- Soil quality
- Grape variety
- Drying techniques
Due to global demand, raisins are widely traded and exported across continents.
Types of Raisins: Comparison with Golden Raisins
Raisins come in several varieties, each with distinct characteristics. The three main types include regular raisins, raisins, and currants.
Regular Raisins
Regular raisins are the most common type and are typically made from seedless grapes.
Key features:
- Sun-dried for several weeks
- Brown to black in color
- Earthy, nutty flavor
- Larger in size than currants
- Lower levels of certain antioxidants compared to golden raisins
They are widely used in baking and everyday snacking.
Golden Raisins (Sultanas)
Raisins stand out due to their controlled drying process.
Key features:
- Light golden color
- Chewy, juicy, and sweet texture
- Milder flavor than dark raisins
- Higher flavonoid antioxidant content
- Popular in both sweet and savory dishes
Their bright appearance also makes them visually appealing in recipes.
Currants (Zante Currants)
Currants are smaller raisins made from ancient Greek grapes.
Key features:
- Dark red to black in color
- Tangy and intense flavor
- Much smaller in size (pea-sized)
- Common in European baking traditions
Currants offer a sharper taste compared to the gentle sweetness of golden raisins.
Nutritional Profile of Golden Raisins
: Raisins are not just tasty—they are packed with concentrated nutrients due to the drying process.
Per 100 grams, raisins provide:
Calories and Carbohydrates
Golden raisins are energy-dense, offering a rich source of carbohydrates that support daily activity and stamina.
Natural Sugars
Their sweetness comes naturally from fruit sugars, making them a healthier alternative to processed candy or desserts.
Dietary Fiber
Raisins contain fiber that supports digestion and helps maintain gut health.
Potassium and Essential Minerals in Golden Raisins
They provide minerals such as potassium, which plays a key role in:
- Heart function
- Muscle performance
- Blood pressure regulation
Comparison with Other Raisins
Compared to regular raisins and currants, golden raisins are often considered superior because they offer:
- Higher antioxidant flavonoid levels
- A softer, juicier texture
- A slightly lower sugar concentration than regular raisins
Why They Are Energy-Dense
Since grapes lose water during drying, their nutrients and sugars become more concentrated. This makes raisins an excellent quick-energy snack when eaten in moderation.
Health Benefits of Golden Raisins
Raisins are nutrient-dense because drying concentrates the natural sugars, fiber, and minerals found in grapes. When consumed in moderation, they offer several impressive health benefits.
Supports Digestive Health
One of the most well-known benefits of golden raisins is their positive impact on digestion.
- Raisins contain a good amount of dietary fiber, which helps add bulk to stool.
- This fiber supports smoother bowel movements and reduces the risk of constipation.
By promoting gut regularity, raisins can contribute to a healthier digestive system and improved overall comfort.
Provides Natural Energy
Golden raisins are an excellent source of quick, natural energy.
- They contain natural fruit sugars such as glucose and fructose.
- These sugars provide an immediate energy boost without the need for processed snacks.
Because of this, raisins are an ideal snack for:
- Busy professionals
- Students
- Athletes
- Anyone with an active lifestyle
A small handful can help fight fatigue and keep energy levels stable throughout the day.
Helps Maintain Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Although raisins are naturally sweet, golden raisins may still support healthier blood sugar control when eaten properly.
- Their soluble fiber slows down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream.
- This helps prevent rapid sugar spikes compared to refined sweets.
Golden raisins can be a better alternative to candy or sugary desserts, especially when paired with protein or healthy fats like nuts.
Promotes Heart Health
: Raisins contain nutrients that support cardiovascular wellness.
- Potassium plays an important role in balancing blood pressure by counteracting excess sodium.
- Fiber helps reduce levels of LDL cholesterol, often called “bad cholesterol.”
Regular inclusion of fiber-rich foods like golden raisins may contribute to better heart function and reduced cardiovascular risk.
Rich in Antioxidants
Raisins are packed with protective plant compounds, including:
- Flavonoids
- Polyphenols
These antioxidants help defend the body from oxidative stress, which is linked to aging and many chronic conditions. Antioxidants work by neutralizing harmful free radicals that can damage cells over time.
Boosts Immunity
Golden raisins also support immune function thanks to their nutrient content.
- Vitamins such as C and E help strengthen the body’s natural defense system.
- Their antioxidant compounds may also protect brain cells from free radical damage.
This combination supports not only immunity but also long-term cognitive health.
Golden Raisins May Reduce Risk of Chronic Diseases
Research suggests that diets rich in antioxidant-containing foods may reduce the risk of chronic illnesses.
raisins, due to their polyphenols and fiber, may be associated with a lower risk of:
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Certain cancers
While they are not a cure, they can be a supportive part of a healthy lifestyle.
Culinary Uses of Golden Raisins
raisins are loved worldwide because they fit into countless recipes. Their sweet yet mild flavor makes them suitable for both desserts and savory meals.
Baking and Desserts
Golden raisins are especially popular in baking because they add moisture and sweetness naturally.
Common uses include:
- Cookies
- Cakes
- Muffins
- Raisin bread
Their plump texture makes baked goods softer and more flavorful.
Breakfast Additions
Golden raisins are a simple way to enhance everyday breakfasts.
They pair perfectly with:
- Oatmeal
- Yogurt bowls
- Granola mixes
- Smoothie toppings
They provide a natural sweetness without the need for added sugar.
Golden Raisins Salads
Adding raisins to salads creates an enjoyable contrast of flavors.
- Their sweetness balances savory greens and dressings.
- Their chewiness adds texture alongside crunchy vegetables or nuts.
They work especially well in Mediterranean-style salads.
Rice and Grain Dishes
Golden raisins are commonly used in rice dishes across Middle Eastern and South Asian cuisines.
Popular examples include:
- Pilafs
- Biryanis
- Couscous dishes
They add small bursts of sweetness that complement spices beautifully.
Sauces, Chutneys, and Stuffed Dishes
Raisins are also excellent in savory preparations.
- Used in chutneys for a sweet-tangy flavor
- Added to sauces for depth and richness
- Included in stuffing recipes for meats or vegetables
Their versatility makes them a favorite ingredient in global cooking traditions.
How to Include Golden Raisins in a Healthy Diet
Incorporating raisins into daily meals is easy and enjoyable.
Some simple and healthy ideas include:
- Snack on raisins with almonds or walnuts
- Add them to yogurt or oatmeal for natural sweetness
- Mix them into a homemade trail mix
- Sprinkle over salads or grain bowls
- Use them in baking instead of refined sugar-heavy toppings
Golden raisins can satisfy sweet cravings while also providing nutrients.
Recommended Daily Intake and Precautions
Raisins are healthy, but portion control is important.
Suggested Daily Serving
- Around 30–40 grams per day
- Roughly a small handful
Benefits of Moderation
Eating raisins in the right amount provides energy and nutrients without excessive sugar intake.
Possible Issues with Overconsumption of Golden Raisins
Too many raisins may cause:
- Digestive discomfort due to high fiber
- High-calorie intake
- Potential weight gain over time
Sulfite Sensitivity
Some golden raisins are treated with sulfur dioxide to preserve color. Individuals sensitive to sulfites should check labels carefully.
Best Golden Raisins in the Market
Choosing high-quality raisins ensures better taste and freshness.
Why Brand Quality Matters
Good brands focus on:
- Proper drying methods
- Hygiene and safety
- Fresh packaging
- Minimal additives
Popular Trusted Brands Worldwide
Some well-known raisin brands include:
- Sun-Maid
- Dole
- Cala
What to Look For When Buying
- Bright golden color
- Soft and plump texture
- Airtight, well-sealed packaging
- No excessive added preservatives
High-quality golden raisins taste better and retain more nutritional value.
Conclusion
Raisins are a powerful combination of flavor, nutrition, and versatility. They provide natural energy, support digestion, offer antioxidant protection, and contribute to heart and immune health.
Whether enjoyed as a snack, mixed into breakfast bowls, baked into desserts, or added to savory dishes, golden raisins remain one of the most valuable dried fruits available.
Including them in balanced meals is a simple and delicious way to enhance both nutrition and taste in everyday life.